Impedance-Based Analysis of Grid-Synchronization Stability for Three-Phase Paralleled Converters
Abstract:
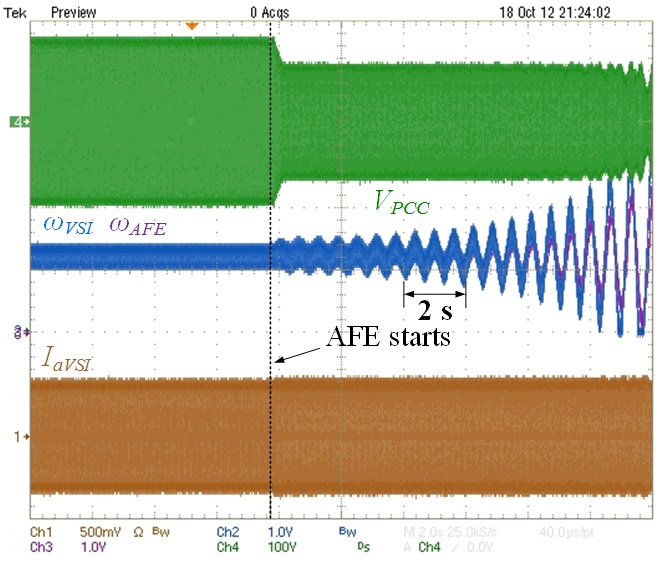
Grid synchronization stability issues and subsynchronous oscillations between synchronous generators exist in electrical power systems. Three-phase voltage-source converters (VSCs) are being installed more and more in the grid to improve efficiency or to utilize renewable energy sources. The same stability issues between VSCs are also reported and analyzed using a small-signal model of phase-locked loops (PLLs). This paper proposes a different impedance-based analysis method. The proposed method shows that synchronization instability in a VSC system is due to the negative incremental resistance behavior of grid-tied inverters’ impedance when they are modeled in the d-q frame. System can be stabilized simply by changing the inverter’s PLL design. Experimental results verify the analysis and the proposed method.
Citation
@article{wen2015,
author = {Wen, Bo},
title = {Impedance-Based {Analysis} of {Grid-Synchronization}
{Stability} for {Three-Phase} {Paralleled} {Converters}},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics},
date = {2015-04-03},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7079502},
doi = {10.1109/TPEL.2015.2419712},
langid = {en}
}